Venous insufficiency causes the legs to feel okay in the morning but progresses to a dragging sensation as the day goes on. The legs become heavy, achy, and fatigued after a few hours. Prolonged car rides, travel, or standing can lead to swollen feet and ankles. These common symptoms should not be ignored as they may indicate venous insufficiency, which can be a highly uncomfortable condition in the future.
When a person's veins have faulty valves, it results in venous insufficiency. This means that the veins are less effective in returning blood to the heart.
Various factors can cause venous insufficiency, with the most common being blood clots (deep vein thrombosis) and varicose veins. Even if you have a family history of the condition, there are simple steps you can take to reduce your chances of developing venous insufficiency.
What is Venous Insufficiency?
To understand venous insufficiency, we need to know how veins function. Veins have small, internal one-way valves designed to return used, deoxygenated blood to the heart. When the valves are insufficient, the veins are no longer able to fulfill this role effectively, leading to blood pooling in the legs. Sometimes, blood may flow toward the feet instead of the heart, a condition known as "reflux." Reflux can manifest in various ways, and it occurs when the two flaps of the bicuspid valves fail to seal properly due to vein injury or dilation. When the valves don't function properly, blood flows back into the veins instead of forward to the heart. Consequently, blood pools in the veins, most commonly in the legs and feet.
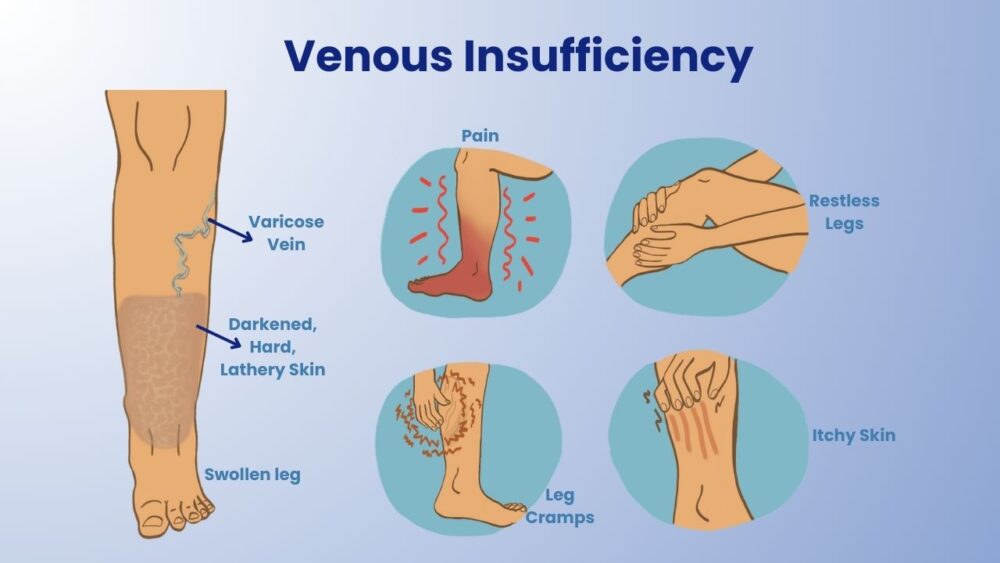
Common symptoms of venous insufficiency include:
Causes of Venous Insufficiency
The following factors are more likely to cause venous insufficiency:
Types of Venous Insufficiency
Categorized into three stages based on the severity of symptoms:
- Stage 1: Characterized by swelling and changes in skin pigmentation.
- Stage 2: Characterized by swelling, changes in skin pigmentation, and dermatitis.
- Stage 3: Characterized by swelling, changes in skin pigmentation, varicose veins, and ulcers.
If venous insufficiency is not treated, the pressure and swelling in the legs will increase to the point where the tiny blood vessels (capillaries) burst. This leads to reddish-brown skin appearance, which becomes extremely vulnerable to damage from bumps or scratches.
Burst capillaries can cause local tissue irritation and damage. In the worst-case scenario, it results in ulcers, which are open sores on the skin's surface. Venous stasis ulcers caused by venous insufficiency can be difficult to heal and prone to infection. If an infection is not treated and spreads to surrounding tissue, it can result in cellulitis. It is commonly associated with twisted varicose veins and swollen veins on the skin's surface, which can occur practically anywhere but are most frequent in the legs.
How is Venous Insufficiency diagnosed?
To diagnose Venous Insufficiency, your doctor will perform a thorough medical history review and physical examination. During the examination, the doctor will thoroughly assess your legs. A vascular or duplex ultrasound test may be used to evaluate the blood circulation in your legs. This test involves placing a transducer (small hand-held device) on the skin above the vein being examined. The transducer emits sound waves that bounce off the vein. These sound waves are recorded, generating an image of the vessel displayed on a monitor.
The appropriate treatment for venous insufficiency depends on the individual and factors such as the cause, symptoms, age, and overall health.
Here are some treatment options for venous insufficiency:
Nonsurgical treatment options:
Compression stockings: These stockings aid in reducing edema and improving blood flow. It is important to remove and wash the stockings at the end of the day, ensuring they fit properly to avoid obstruction of blood flow.
Sclerotherapy: This procedure involves injecting a solution directly into spider veins or varicose veins, causing them to collapse and dissolve. Multiple treatments may be necessary to achieve desired results. Sclerotherapy can relieve pain and discomfort while reducing the risk of complications.
Endovenous Laser Ablation: This procedure uses laser or high-frequency radio waves to produce localized heat in the abnormal vein, sealing it shut. It causes minimal bleeding and bruising, results in less pain and complications compared to ligation and stripping, and allows for a faster return to regular activities while maintaining cosmetic benefits.
Surgical treatment options:
Ambulatory Phlebectomy: This minimally invasive treatment involves making micro-incisions or needle punctures over the veins and removing the problematic veins using a fine phlebectomy hook.
To reduce the chances of developing Venous Insufficiency, follow these tips:
To prevent or manage venous insufficiency, it is best to seek timely assessment and treatment from a doctor. Dr. Niloofar Yazdani, with over 18 years of experience as a medical practitioner, can provide the necessary expertise. Dr. Nellie has a high success rate and understands your concerns. Visit Melbourne Varicose Vein Clinic for more information.
Contact us at +03-9885-4494 or send an email to enquiry@melbournevein.com.au.


